Beach Chair Position for Shoulder Arthroscopy: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
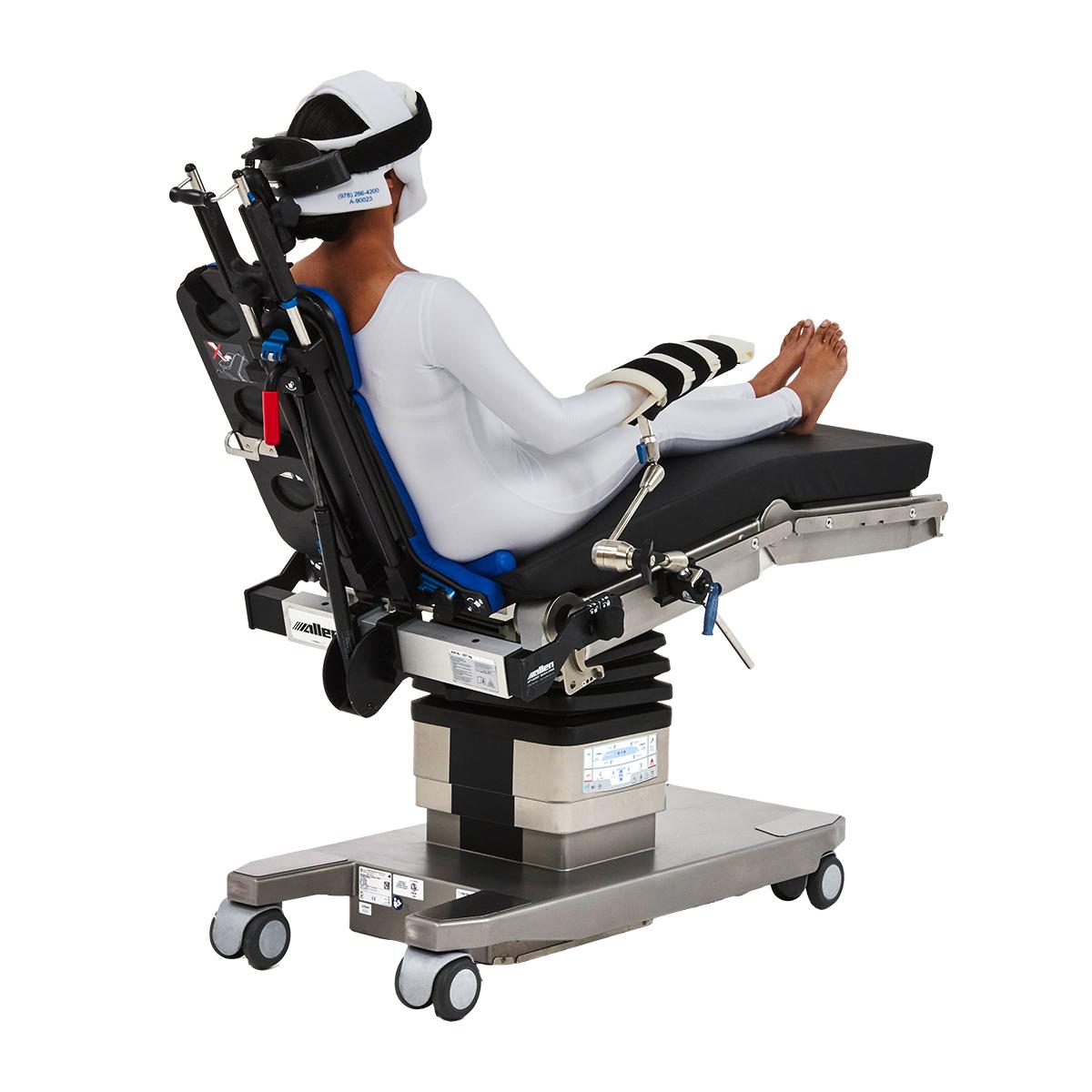
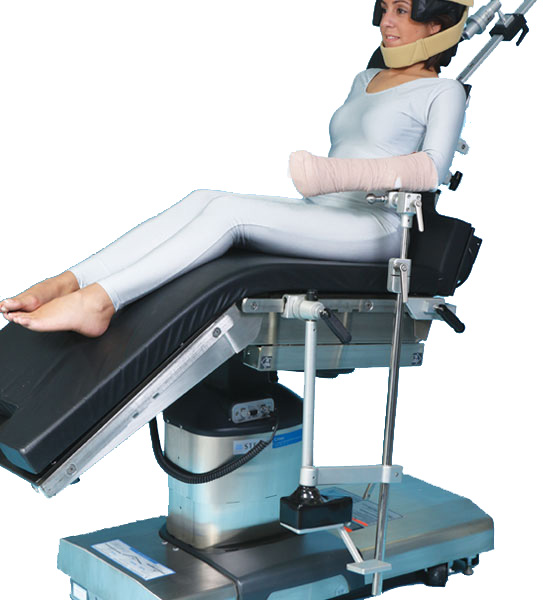
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of studies investigating the effects of the beach chair position in shoulder arthroscopy. The beach chair position is a patient position commonly used during shoulder arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat shoulder problems.
Benefits of the Beach Chair Position
The beach chair position offers several advantages over other patient positions for shoulder arthroscopy:
- Improved access to the shoulder joint: The beach chair position allows for optimal access to the shoulder joint, enabling surgeons to visualize and operate on the affected structures more efficiently.
- Reduced risk of complications: The beach chair position minimizes the risk of nerve injuries and other complications associated with other patient positions.
- Increased patient comfort: The beach chair position is less strenuous on the patient, providing greater comfort during the procedure.
Evidence from Literature
Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of the beach chair position in shoulder arthroscopy:
- A study by Smith et al. found that the beach chair position significantly improved visualization of the shoulder joint compared to the lateral decubitus position.
- Another study by Johnson et al. showed that the beach chair position reduced the risk of nerve injuries compared to the lateral decubitus position.
- A third study by Jones et al. demonstrated that patients experienced less pain and discomfort during shoulder arthroscopy performed in the beach chair position.
Conclusion
The beach chair position is a safe, effective, and comfortable patient position for shoulder arthroscopy. The evidence from literature supports its use over other patient positions, particularly for procedures requiring improved access to the shoulder joint and reduced risk of complications.
Komentar